
MELD SCORE Mnemonic CBI Medshorts Yt shorts Mis.Medicine YouTube
The new MELD scores are calculated first by determining the traditional MELD score as an initial score (MELD (i) ); if the initial MELD (i) score is 12 or greater, the score is adjusted by incorporating the serum sodium value. MELD Serum Bilirubin (mg/dL): INR (International Normalized Ratio): Serum Creatinine (mg/dL):
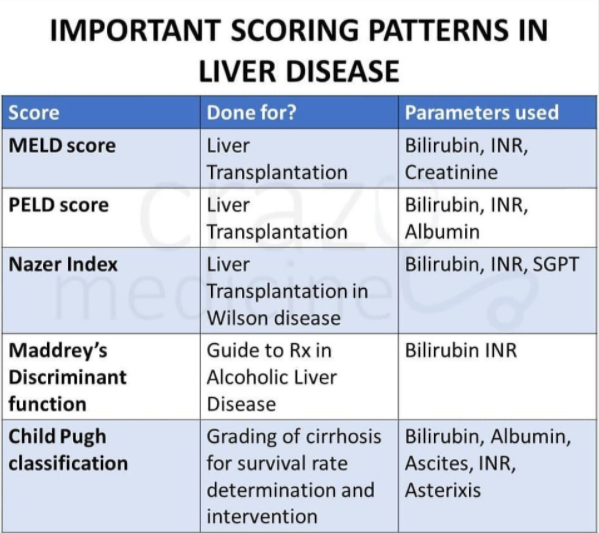
Important Scoring Systems in Liver diseases Indication and Components
In the validation set, the median MELD 3.0 score was 19 (IQR, 13-26), with 3.4% of subjects having scores of >40. Of 8823 candidates in the set, 318 died within 30 days and 514 within 90 days. The C-statistic for 90-day mortality of MELD 3.0 was 0.8693, and that of MELDNa was 0.8622 (the method of Harrell et al. 12.

Determining the Severity of Acute Pancreatitis [UndergroundMed] YouTube
MELD scores are reported as whole numbers - the equation result is rounded UNOS has made the following modifications to the score: if the patient has been dialyzed twice within the last 7 days, then the factor for serum creatinine used should be 4.0
Meld score mnemonic rytedigest
Introduction: The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) is a prognostic score to measure the severity of liver failure and thus to estimate short term survival in patients with chronic liver disease. It has been used to determine priorities in organ allocation for patients awaiting liver transplantation in the United States since 2002.

MELD Score calculator APK for Android Download
The MELD score accurately predicts 90-day mortality risk in patients with cirrhosis and provides the first objective criteria to equitably prioritize patients on the liver transplant waiting list. However, as the epidemiology of liver disease shifts, the MELD score is losing its predictive ability. In addition, the current score disadvantages.

ladergray Blog
Background. Since its original description, the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) has proven to be a reliable predictor of short-term survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. 1 The current version of the MELD score, commonly referred to as MELDNa, incorporates serum concentrations of total bilirubin, creatinine and sodium, and the international normalized ratio (INR) of.
202 LIVE! Lymphadenopathy Taking Your Lumps The Curbsiders
The model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score is an established indicator of cirrhosis severity and a predictor of morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) creation and for allocation in liver transplantation. Since the adoption of the score, its use has been expanded to multiple new indications requiring model modifications.

[PDF] Current management of the complications of portal hypertension variceal bleeding and
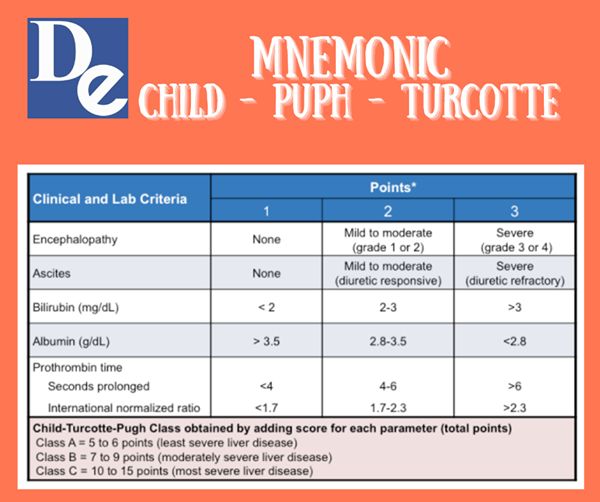
MELD Score; MELD-Plus; History. The surgeon and portal hypertension expert Charles Gardner Child (1908-1991) (with Turcotte) of the University of Michigan first proposed the scoring system in 1964 in a textbook on liver disease. It was modified by Pugh et al. in 1972 in a report on surgical treatment of bleeding from esophageal varices.
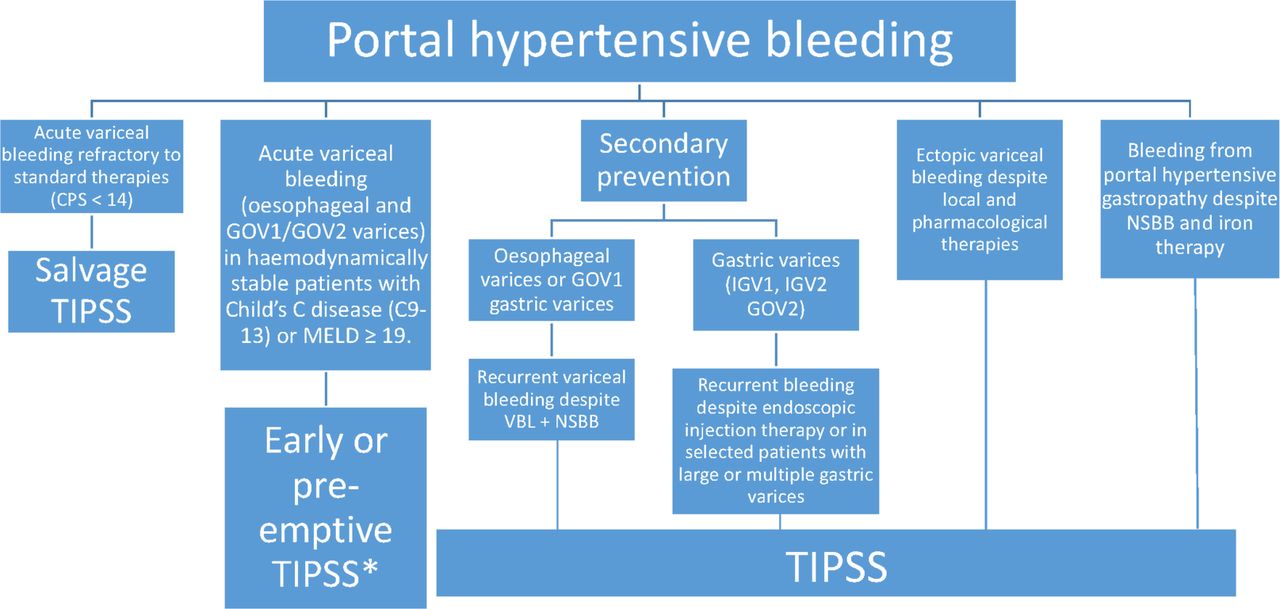
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stentshunt in the management of portal hypertension Gut
The MELD score ( Model for End-stage Liver Disease ) is a classification used to grade liver dysfunction in preparation for liver transplantation. The score has prognostic value in terms of three month mortality and certain complications. The components of the score are: serum creatinine (mg/dl)

Performances of MELD, MELDNa, and PELD scores, INR, TB serum level,... Download Scientific
Child-Pugh and MELD scores have been widely used for the assessment of prognosis in liver cirrhosis. A systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to compare the discriminative ability of Child-Pugh versus MELD score to assess the prognosis of cirrhotic patients. PubMed and EMBASE databases were searched.

MELD Score Calculator Liver Disease App iMedical Apps
It is calculated according to the following formula: MELD = 3.78×ln [serum bilirubin (mg/dL)] + 11.2×ln [INR] + 9.57×ln [serum creatinine (mg/dL)] + 6.43 MELD scores are reported as whole numbers - the equation result is rounded UNOS has made the following modifications to the score:

Medicowesome January 2018
MELD score mnemonic Hello everyone! Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) is a reliable measure of mortality risk in patients with end-stage liver disease. It is used as a disease severity index to help prioritize allocation of organs for transplant.

MELD Score for Liver Disease How is the MELD score used to diagnose liver disease? 247nht
A MELD score was originally used to predict three-month survival in end-stage liver disease, largely replacing the Child-Turcotte-Pugh system. MELD scores were adopted by the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) in 2002 to help prioritize people waiting for a liver transplant. In 2016, serum sodium was added to the MELD score formula, with.

CHILDPUGH VS MELD SCORE OF LIVER DISEASE MNEMONIC شرح باطنة مبتكرسهل سريع نيمونكس YouTube
The original MELD score is a prospectively developed and validated chronic liver disease severity scoring system that uses a patient's laboratory values for serum bilirubin, serum creatinine, and the international normalized ratio (INR) for prothrombin time to predict three-month survival ( original MELD score ).

The LTRS incorporates age, the MELD score, the BMI, and the presence of... Download Scientific
The MELD score ranges from 6 to 40, and is a measure of how severe a patient's liver disease is. MELD can fluctuate based on your current condition, with variations from a few points as lab values vary to a larger increase if you have an infection or an acute decompensation (worsening of your liver disease). There is also a system of.
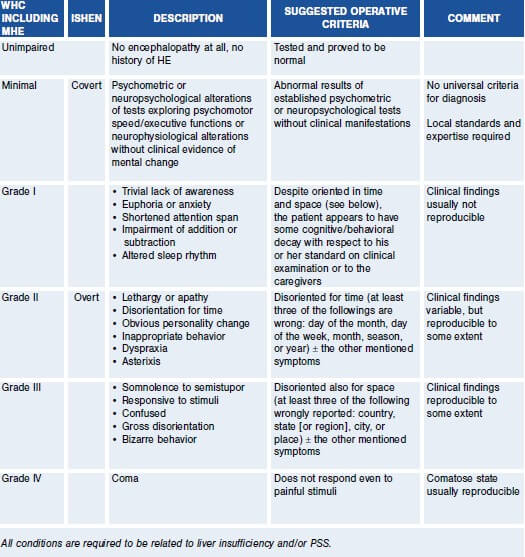
Lula Edwards Headline Childpugh Score Prognosis
The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease, or MELD, is a scoring system for assessing the severity of chronic liver disease.