Bacterial Cell Structure and Function
Label a Bacteria Cell Bacteria are tiny single-celled organisms that are all around us, too small to be seen without a microscope. They're living things that come in different shapes like spheres (called cocci), rods (called bacilli), or spirals. Some of them are helpful, like the ones that help us digest food, while others can make us sick.
Bacterial Cell Structure and Function
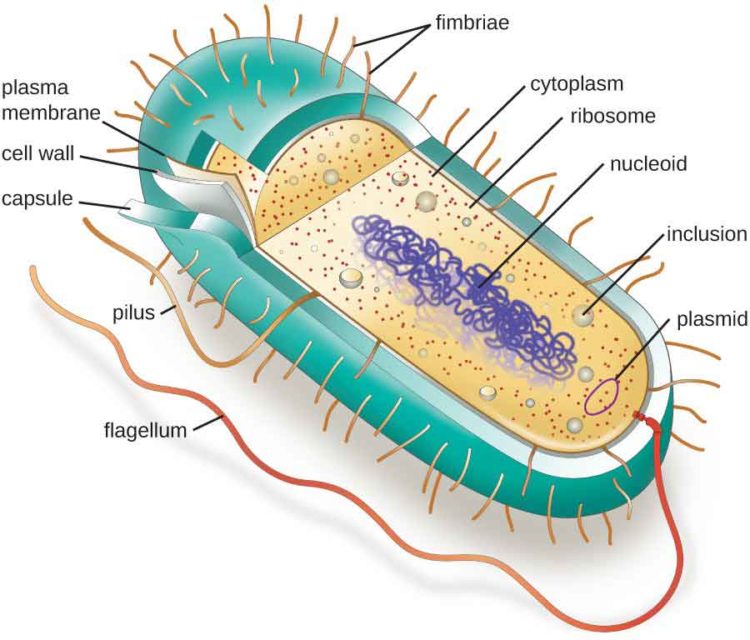
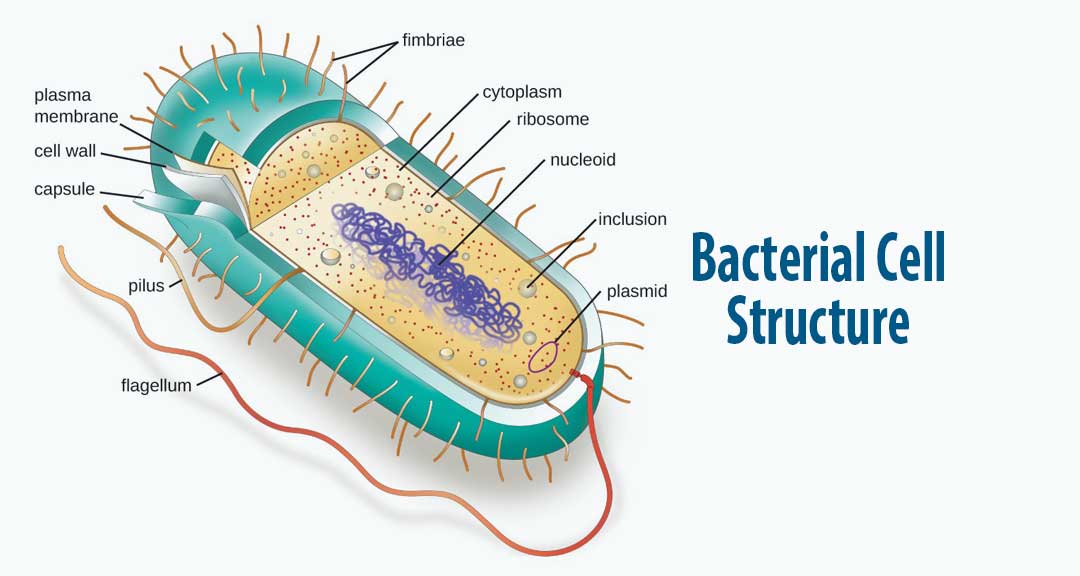
Figure: Labelled diagram of a typical bacterial cell Cell wall. The thick erect elastic membrane that lies beneath the slime layer outside the bacterial cell is called the cell wall. Its thickness is around 10-25 nm and is made up of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. Usually, the cell wall does not contain cellulose.

Bacterial Cell Labeled Images & Pictures Becuo
Bacteria is a unicellular prokaryotic organism. The structure of the bacteria consists of three major parts: Outer layer (cell envelope), cell interior, and additional structures. Outer layer (Cell envelope): It includes the cell wall of bacteria and the plasma membrane beneath it. The outer envelope acts as a structural and physiological.

Bacteria cell anatomy Royalty Free Vector Image
What are prokaryotes? Prokaryotes are microscopic organisms belonging to the domains Bacteria and Archaea, which are two out of the three major domains of life. (Eukarya, the third, contains all eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi.) Bacteria and archaea are single-celled, while most eukaryotes are multicellular.
Bacteria Cell Vector Art, Icons, and Graphics for Free Download
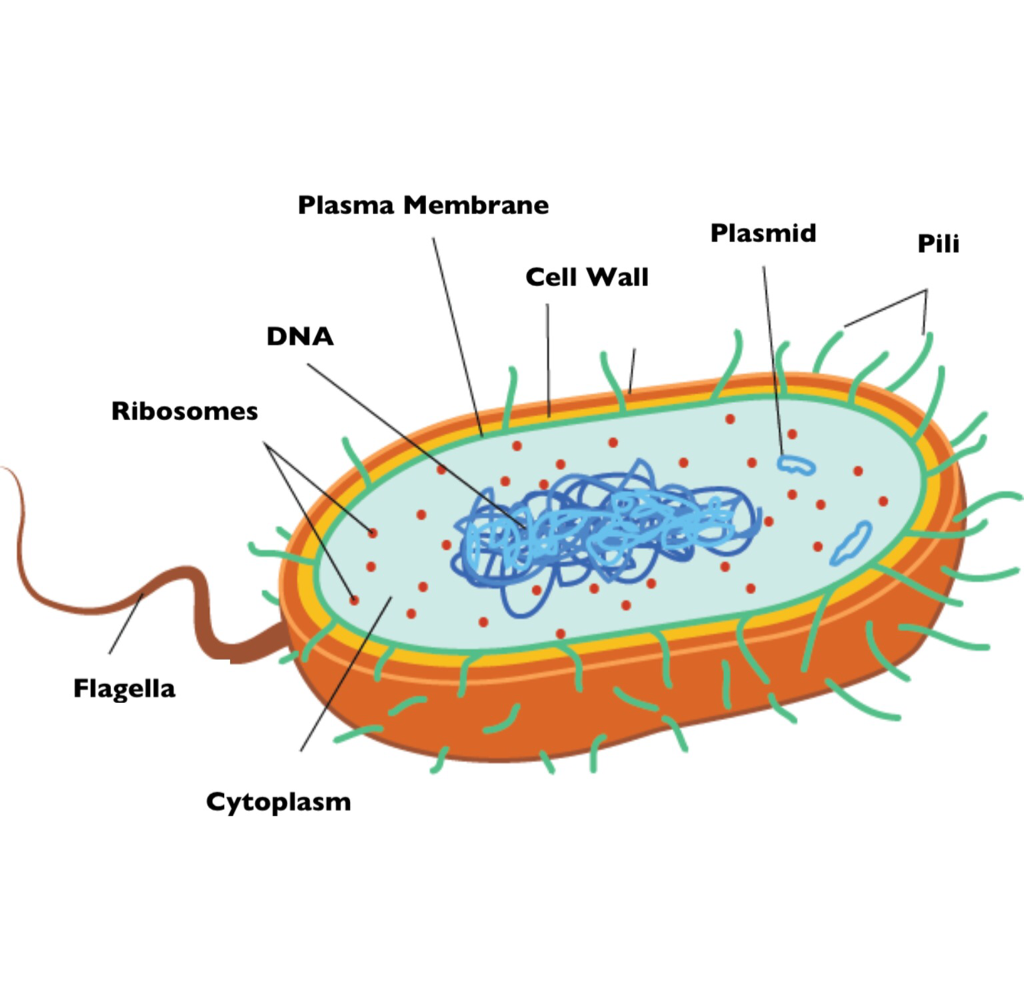
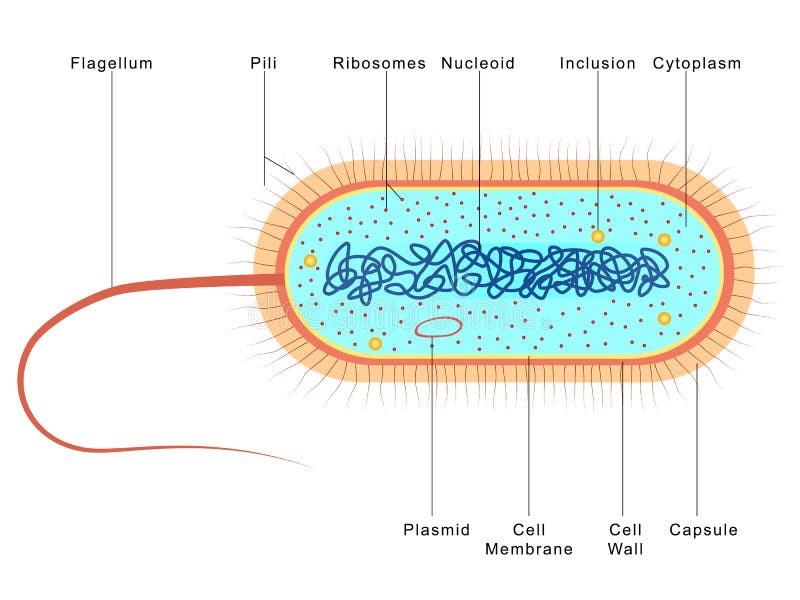
In this article we will discuss about the cell structure of bacteria with the help of diagrams. A bacterial cell (Fig. 2.5) shows a typical prokaryotic structure. The cytoplasm is enclosed by three layers, the outermost slime or capsule, the middle cell wall and inner cell membrane. The major cytoplasmic contents are nucleoid, plasmid, ribosome.
Bacteria Labeled Diagram Stock Vector Art & Illustration, Vector Image 78697031 Alamy
bacteria, any of a group of microscopic single-celled organisms that live in enormous numbers in almost every environment on Earth, from deep-sea vents to deep below Earth's surface to the digestive tracts of humans. Bacteria lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other internal structures and are therefore ranked among the unicellular life-forms.

prokaryotic cell bacteria parts
All bacteria, both pathogenic and saprophytic, are unicellular organisms that reproduce by binary fission. Most bacteria are capable of independent metabolic existence and growth, but species of Chlamydia and Rickettsia are obligately intracellular organisms. Bacterial cells are extremely small and are most conveniently measured in microns (10-6 m). They range in size from large cells such as.
Bacteria Grade 11 Biology Study Guide
Bacteria - Definition, Structure, Diagram, Classification: Bacteria are truly fascinating microorganisms with an incredible ability to adapt and thrive in diverse environments. From their unique structures to their various nutritional and reproductive strategies, they play essential roles in shaping our world.
Bacteria Ms A Science Online
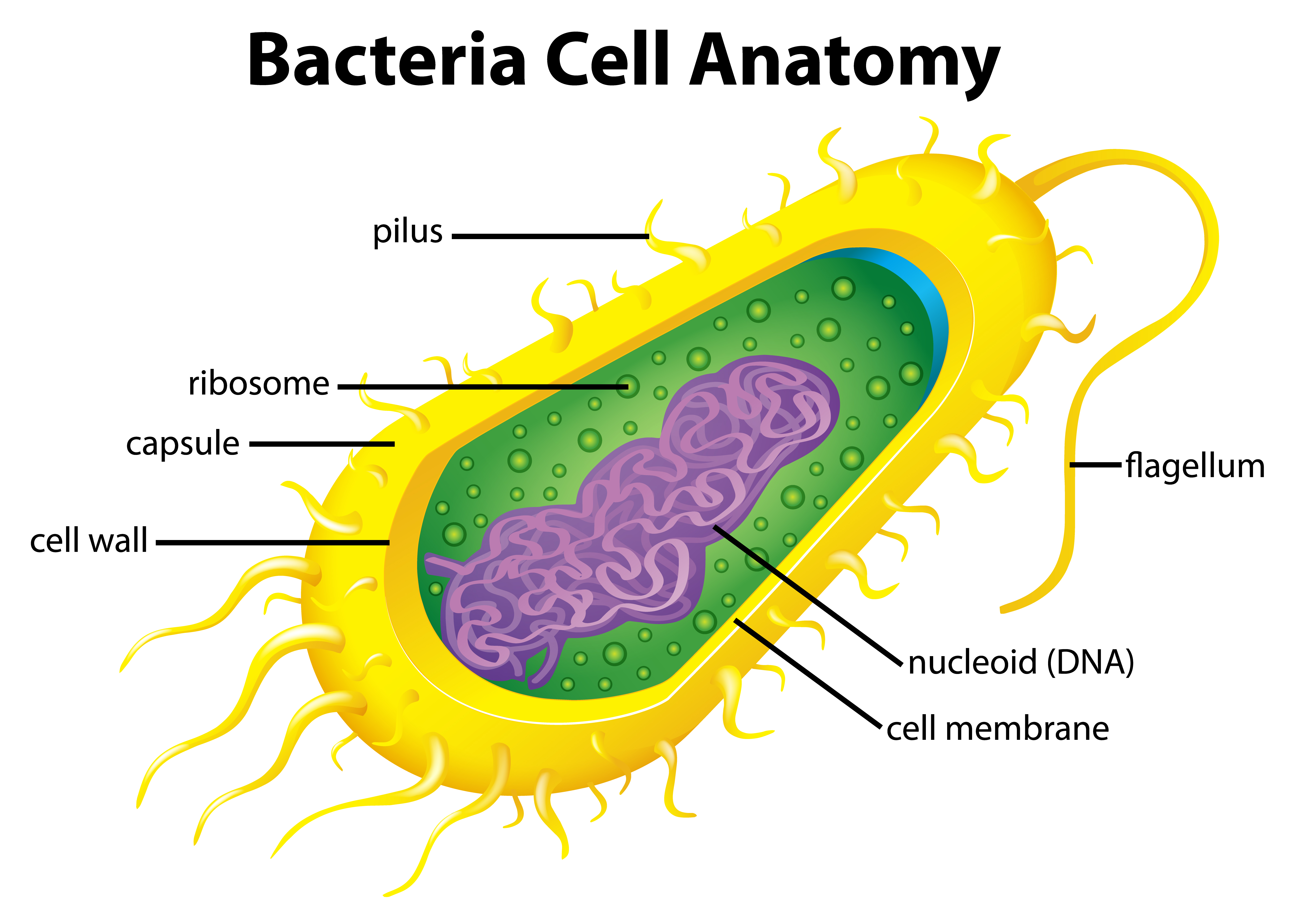
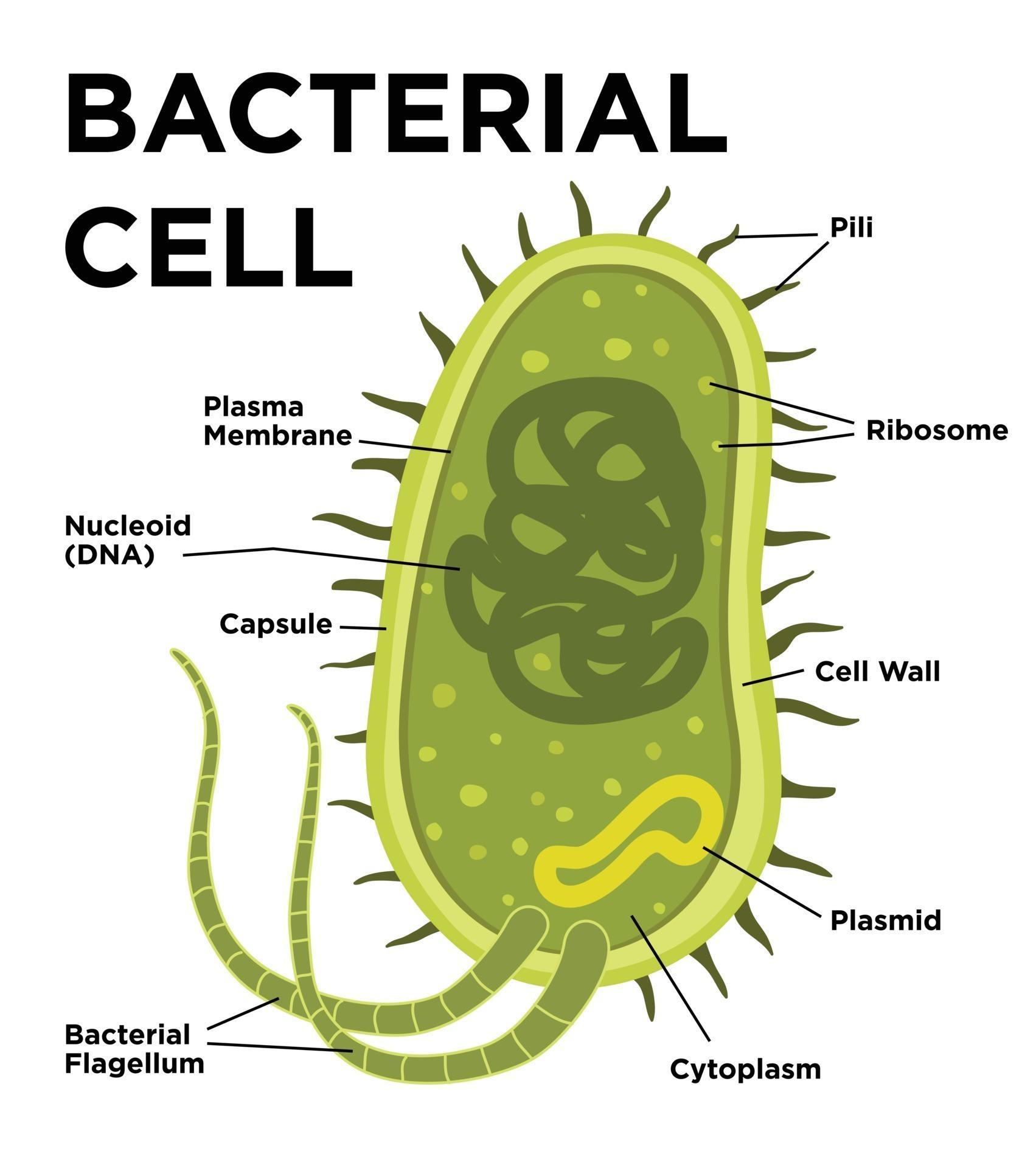
1. A bacterial cell remains surrounded by an outer layer or cell envelope, which consists of two components - a rigid cell wall and beneath it a cytoplasmic membrane or plasma membrane. ADVERTISEMENTS: 2.

Bacterial Structure Plantlet
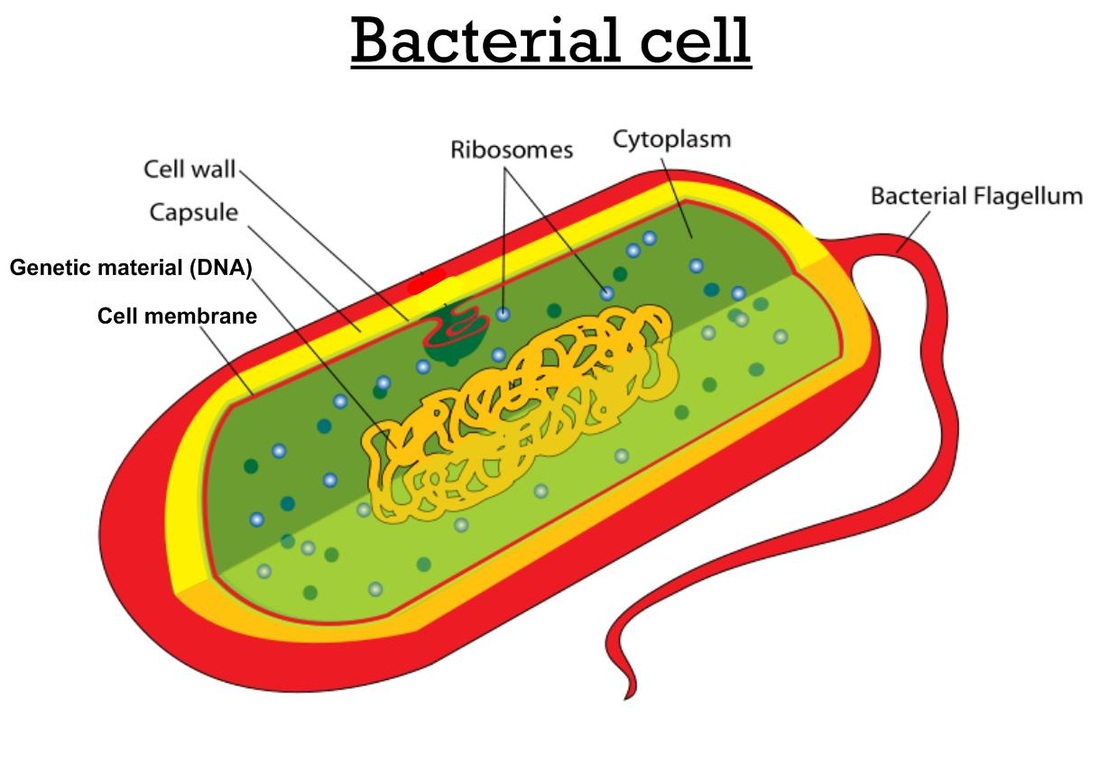
Cell Envelope - The cell envelope is made up of two to three layers: the interior cytoplasmic membrane, the cell wall, and -- in some species of bacteria -- an outer capsule. Cell Wall - Each bacterium is enclosed by a rigid cell wall composed of peptidoglycan, a protein-sugar (polysaccharide) molecule. The wall gives the cell its shape and.
Anatomy of Bacteria stock vector. Illustration of labelled 43965779
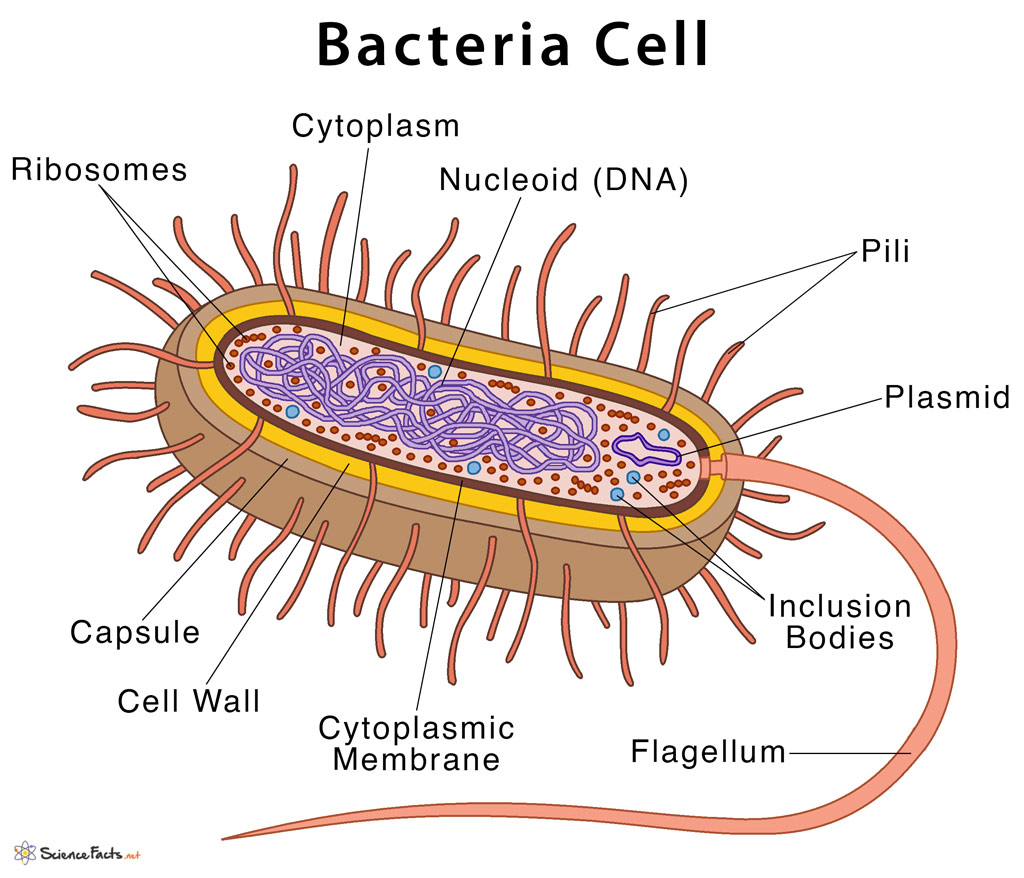
Bacteria Diagram with Labels Bacterial cells have simpler internal structures like Pilus (plural Pili), Cytoplasm, Ribosomes, Capsule, Cell Wall, Plasma membrane, Plasmid, Nucleoid, Flagellum, etc. Labeled Bacteria diagram Eukaryotes have been shown to be more recently evolved than prokaryotic microorganisms.

Bacterial cell structure Year 12 Human Biology
The bacteria shapes, structure, and labeled diagrams are discussed below. Table of Contents [ show] Sizes The sizes of bacteria cells that can infect human beings range from 0.1 to 10 micrometers. Some larger types of bacteria such as the rickettsias, mycoplasmas, and chlamydias have similar sizes as the largest types of viruses, the poxviruses.

Structure of Bacteria Cell and its Organelles Study Wrap
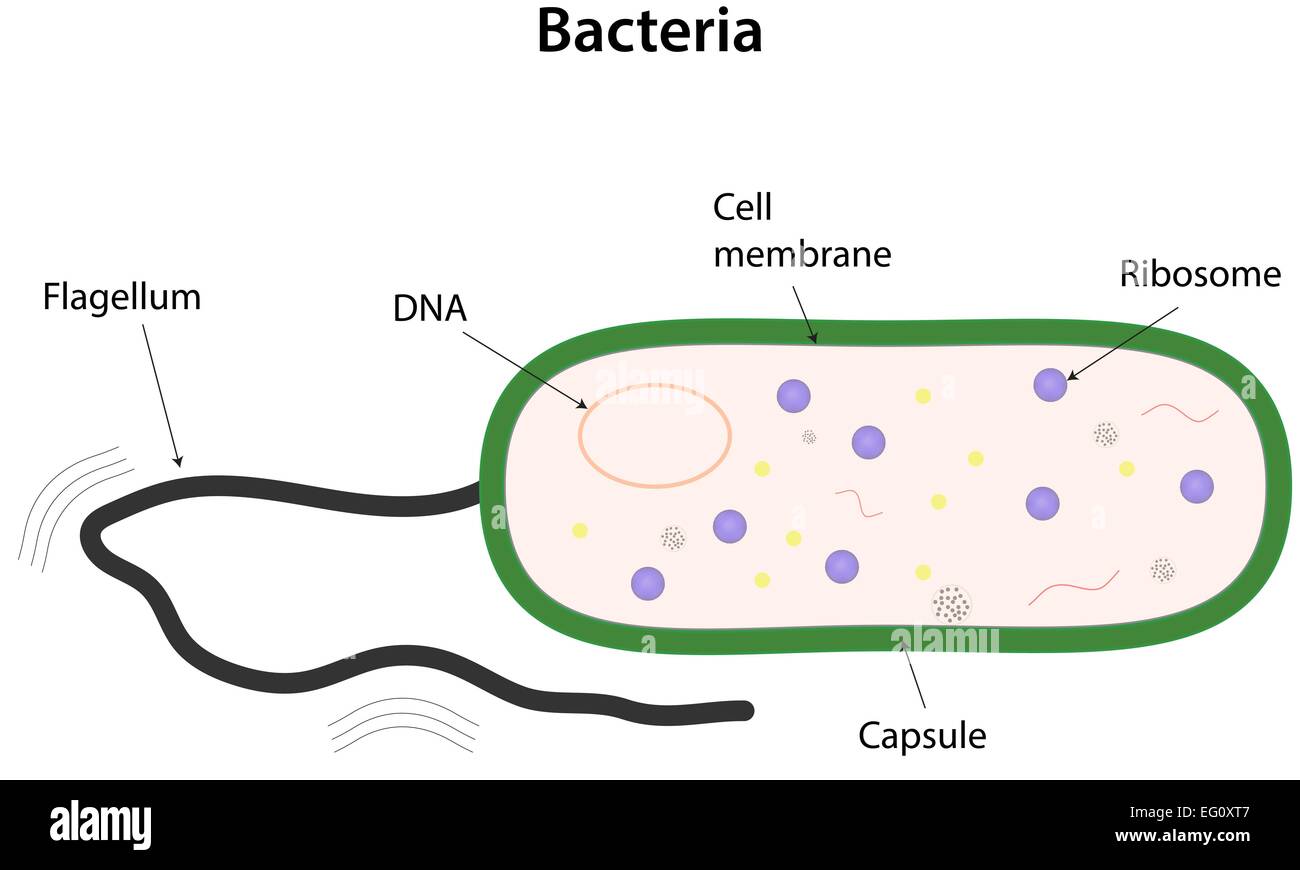
DNA in a nucleus. Plasmids are found in a few simple eukaryotic organisms. Prokaryotic cell (bacterial cell) DNA is a single molecule, found free in the cytoplasm. Additional DNA is found on one.
Bacterial cell anatomy in flat style. Vector modern illustration. Labeling structures on a
Summary edit. English: A simple diagram of a bacterium, labelled in English. It shows the cytoplasm, nucleoid, cell membrane, cell wall, mitochondria (which bacteria lack), plasmids, flagella, and cell capsule. The SVG code is valid. This diagram was created with an unknown SVG tool.
Characteristics of bacterial cells
coccus (circle or spherical) bacillus (rod-like) coccobacillus (between a sphere and a rod) spiral (corkscrew-like) filamentous (elongated) Cell shape is generally characteristic of a given bacterial species, but can vary depending on growth conditions.

Bacterial Structure Plantlet
A prokaryote is a simple, single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.